Mr. Amerman is the creator of a number of DVDs and books on finance, including two books published by McGraw-Hill (and subsidiary): Mortgage Securities, and Collateralized Mortgage Obligations: Unlock The Secrets Of Mortgage Derivatives. He has been a speaker and workshop leader for sponsors including The Institute for International Research, New York University, and many banking groups.
Mr. Amerman has spent a number of years in researching alternatives. Drawing upon his background outside the individual investor industry, he has developed an interrelated group of non-traditional solutions – including asset/liability management strategies – for such concerns as financial crisis, inflation, inflation taxes, low economic growth rates, and pervasive low yield markets.
REVISiTING THE EXPANSION OF FIAT CURRENCY
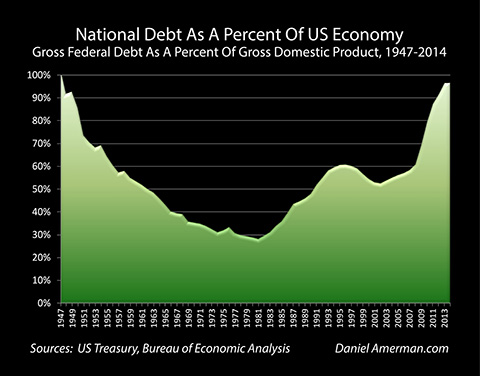
The bigger issue is that we had a change in the national debt super cycle. As of 1947 due to the expense of WWII, the outstanding US debt was approximately equal to the size of the total economy. This is as toxic for a country back in 1947 as it is today.
Historically the growth rate of heavily indebted countries is much slower. It is a slow economic growth and a high interest rate risk environment. This was not just the US alone, this was most definitely global. What world leaders did as a result was get together, and yes Bretton Woods was part of this and they agreed to put rigid financial controls on the population. Effectively the size of national debt was held down for approximately 25 years while the economies experiences periods of substantial growth. Eventually these national debts as a percent of the economy had dropped down to below 30%.
This decline promoted a rapid growth environment, free market interest rate, removal of capital controls, and lifted the limitations on private ownership which we have had since 1973; individuals in the US could not hold gold for investment purposes.
RING FENCING
“You’re not going to keep up with inflation and there is not much you can do about it. That’s the point of ring fencing.”
I split it into two ways. The first is capital controls and second, forcing intermediaries to participate in financial repression. Another component as well is repressing the ownership of precious metals so people do not have an alternative protection from inflation. What’s surprising is that the term financial repression has a conspiracy theory connotation associated with it, when in fact financial repression is an integral part of macroeconomics. It has been a core part of managing financial systems over a long period of time. What’s surprising is that the term financial repression has a conspiracy theory connotation associated with it, when in fact financial repression is an integral part of macroeconomics. It has been a core part of managing financial systems over a long period of time.
In the US in a relatively short period of time, particularly in 2010 all these elements were released for the first time since the 1970s. Interest rates were forced down below inflation by massive government intervention, quantitative easing and forms of capital controls all came out together and as a result dominated the markets ever since. The fascinating part is that there has been a series of developments over the last few months which may be the biggest round of financial repression that we have seen since 2010.
“Ring fencing which I consider as the third pillar is the forced participation of financial intermediaries in the name of public safety. Two key developments were what came out in 2015 was that the Fed has a part of the financial stability board. This board is the G20, the IMF, World Bank combined and all simultaneously agreed to change their money fund policy as well as their margin rules.”
Ring fencing which I consider as the third pillar is the forced participation of financial intermediaries in the name of public safety. Two key developments that came out in 2015 was that the Fed has a part of the financial stability board. This board is the G20, the IMF, World Bank combined and all simultaneously agreed to change their money fund policy as well as their margin rules. They changed regulation on money funds which are apparently done in the name of public safety such that it was an expensive burden for any funds to use anything other than federal debt for their money funds. Effectively creating an enormous financial advantage.
“This is a classic scenario. Take a financial intermediary and in the name of public safety make them hold US government debt.”
This is a classic scenario. Take a financial intermediary and in the name of public safety make them hold US government debt. In doing this you have expanded the market for government debt by whatever the net change is. Essentially locking in an additional trillion dollars of funding for the debt.
“A key thing to make note of is that these are all financial intermediaries, so when people ask who is funding the debt, the answer is all of us are.”
We are essentially financing the government through an intermediary. By changing regulations they are both increasing the relationship and locking into it. At this short term end of the yield curve we are doing this for virtually no yield whatsoever. We are providing the money to the federal government through an intermediary whose participation is forced.
FORCED MACROPRUDENTIAL POLICIES
“They are forcing ever lower interest rates on more of the population. This is providing larger low-cost funds to the government in an ever more constrained manner where it becomes harder for people to escape.”
On Nov 12, 2015 the financial stability board agreed to implement margin rule changes. They were talking about it being a blast from the past, it was what central banks used to do in the 1970s. This is now brought back out, but in this case it is also an expansion of the mandate of the Fed. Where we are with these changes is that the Fed will be without active congress and expanding their control over the US markets to all investment firms to participate in some sort of secured lending.
Financial firms often need cheap money on a short term basis. They can sell a treasury security to someone else at a given price and agree to buy it back at a higher price; in effect it becomes a short term loan. The difference in price is the interest rate that they are paying, this can be done without an actual sale and instead with the pledge of the securities as collateral.
“Central banks are concerned that these low quality collateral loans are now considered to be at risk for triggering a new financial crisis. That’s why they’re changing the regulations where they have the ability to change margin rules at will.”
The best known forms of margin deal with stock ownership where your borrowings become limited. If this was raised to 60% or 70% to bring down stock values, people will have to scramble to sell these securities or they will have to come up with the additional cash through some other means, otherwise there will be a forced liquidation.
What has been created is a major incentive to use US treasuries securities as collateral for repurchase agreements. Once everyone does this then you get a situation where the Fed is no longer in control of leverage in the market.
PREPARING FOR THE FUTURE
Funding for US national debt has just increased by $2.5 trillion. This is very similar to something that is far controversial and that is quantitative easing. Total US treasuries securities held by the Fed are between 2.4 to 2.5 trillion. They are holding this approximate level because they say they are not doing quantitative easing and rather doing purchases every time they take principal to keep at that level. This was major news and made headlines throughout the world, yet something just as big happened and nobody noticed; this is a forced funding of the federal debt that is just as large as what happened with QE.
“The Fed is in the process of deploying two massive stabilizers. Why are they doing this in 2016 when they hadn’t done so in 2010?”
The logical interpretation would be they are very concerned of what’s to unfold in the future. They are pre-emptively moving major stabilizers in place.
To follow Daniel Amerman and his work, please visit http://danielamerman.com/aHome.htm
Abstract written by, Karan Singh
Karan1.singh@ryerson.ca








